Healthcare has been progressing at lightning speed, thanks to the rapid development in deep technology, scientific research, and artificial intelligence. In this discussion of progress, crop up terms like Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR) and Mixed Reality (MR). Each of these open a world of possibilities for medical care, helping doctors, technicians and other healthcare professionals innovate, optimize, and improve the quality of their services.
There are several bleeding-edge gadgets like Google Glass and Microsoft’s HoloLens that are leading the beacon of hope, making virtual and remote healthcare a reality. Before we start digging into the details of MR, here is my quick understanding of VR, AR, and MR and how they are different from each other.
Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality and Mixed Reality

Image source –ARreverie
Virtual Reality is a simulation that allows the user to immerse in a virtual world without having any sense of reality. It occludes your vision, cutting you completely from the physical world. To experience VR, through a VR supported app or game, one needs a suitable system and a compatible device.
Augmented Reality is an overlap of virtual information onto the physical world that enhances the overall usability and experience. Here, the real world remains central to the experience. AR can be experienced even on regular smartphones; it is not dependent on a particular kind of system or device.
Mixed Reality, often termed as hybrid reality, is when the virtual world coincides and interacts with the real world. While AR and VR are popularly used in training and gaming, MR is more relevant for AI-based training. It essentially falls somewhere between augmented reality and augmented virtuality and experiencing it requires you to wear a headset such as HoloLens by Microsoft.
All three of the above play important and distinct, though interrelated, roles in the development of not just healthcare but a variety of fields and industries. In this blog, we will look at MR and its contribution to the future of healthcare.
Mixed Reality in Healthcare
Healthcare has been adopting technological advancements to visibly improve the quality of medical facilities. Artificial Intelligence has been an integral part of this progression and has made it possible for medical professionals to extend remote monitoring and care to patients. It has also helped them optimize their resources and make them better available to patients.
A lot of time, money, and effort is being invested in mixed reality in healthcare, which shows that we will be able to see some great breakthroughs very soon. Incorporating MR into healthcare will allow sharing of patient records and data in a more interactive form. Also, it will play a major role in letting students train using MR applications, which will motivate and encourage them to explore and learn without the fear of failure. In the near future, I believe we could also see MR being used to plan critical surgeries.
As a key device to experience MR, the latest product from Microsoft is HoloLens 2. It is a combination of MR and AI, designed to offer an immersive and clear view in the form of holograms. It has a large and high-resolution display that gives a full picture of surroundings. It is an intuitive device that facilitates collaboration from multiple locations. You can also combine it with other Microsoft apps to expand its capabilities. The HoloLens 2 is a comfortable headset that can be used for long hours with minimal eye fatigue. Along with GigXR‘s HoloHuman and HoloPatient, HoloLens allows medical students to learn by interacting with a holographic patient via virtual and augmented reality.
HoloPatient offers a 3D holographic video of actual standardized clinical patients. It is the latest in immersive technology that creates a safe-to-fail learning environment for medical students where they can observe the same patient, consult together, review test results and discuss assessment and diagnosis.
HoloHuman, on the other hand, is the world’s first 3D anatomy model created for immersive exploration. It allows medical students to access a range of models by just putting on the headset and selecting from thousands of anatomical structures. It can be used to perform virtual cadaveric dissections and discover the inside of organs such as the heart and brain in greater detail by simply stepping towards the model, ‘opening up’ the anatomy to reveal its internal structures. It is a user-friendly device that is easy to navigate and explore. You can even highlight, hide, or fade the images for better view and understanding.
Application of Mixed Reality in Healthcare
With so much happening in Mixed Reality (MR) with respect to medical care, I believe it could be used in several ways by doctors, technicians, and even medical professors. Some of the leading areas where putting MR apps to use will give us some amazing results:
- Real-time Access to Medical Data – MR headsets have the capability to provide relevant medical information in real-time. It can be critical in case of emergencies as quick data can alert doctors to take quick action.
- Remote Patient Care – Having access to real-time data will allow hospitals to provide hospital level care to patients at home. It will make patients more comfortable and reduce the load on in-the-hospital resources.
- Better Utilization of Resources – With remote patient monitoring, freed resources can be used to attend to more critical patients.
- Better Imaging – MR can help professionals view 3D images in a better and more natural way. The depth can be visualized better seamlessly, allowing for clearer analysis of the details.
- Live Streaming – Using MR, surgeries can be streamed live as well as recorded, allowing a great learning opportunity for students of surgery. It is the closest they can get to viewing a real surgery without having to go to the operation theatre (OT). Besides giving them a view of what happens in an OT, the recording lets them go back for details and nuances of various steps and techniques.
- Streamlining Information Dissipation – MR can be used for several tasks, including streamlining information storage and sharing. MR technology can make sharing of critical medical information seamless and available to all in the same format. It can eliminate dependence on multiple devices making communication smoother.
- Patient Education – MR application also provides virtual surgery intelligence (VSI) to physicians making it easier for them to educate patients about the surgery, and show them the level of complication involved in the process. It goes a great way in preparing patients for the surgery and making them feel confident about the procedure. It helps improve surgical accuracy as well.
- Remote Surgery Assistance – Using MR headsets such as HoloLens, surgeons can use microphones and sensors to connect and collaborate with surgeons around the world. They can seek assistance remotely and execute better.
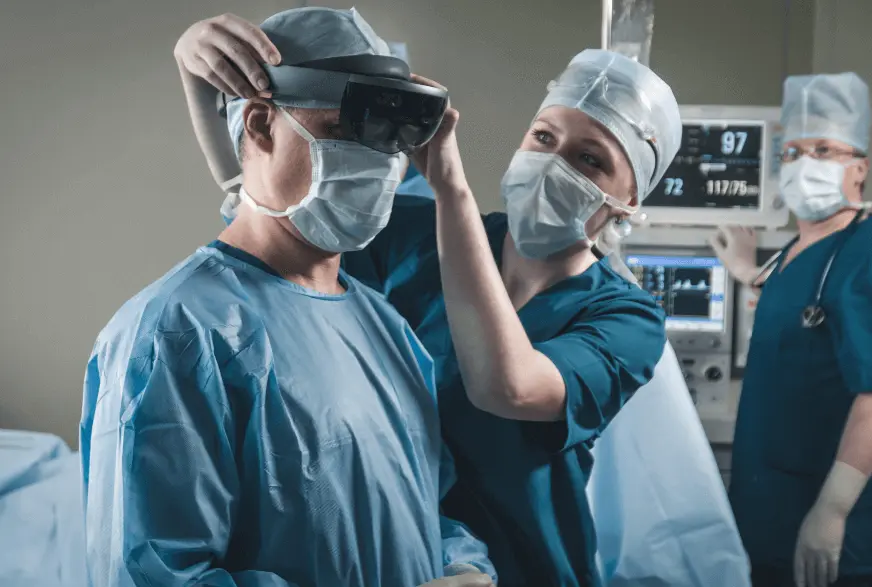
Using technology to see live surgeries and procedures will educate them more than a classroom, a textbook or even a PPT can ever do. As of now, incorporating MR has been limited and restricted due to several reasons. However, there are some great stories that show us how MR is helping us improve healthcare, rapidly and steadily.
Recently a leading pharmacy and medication management organization, offering automation and business analytics software solutions for patient-centric medication, wanted to accelerate innovation. They wanted to achieve its vision of delivering Pharmacy Automation by building a Mission Control Center (MCC) to monitor its autonomous pharmacy devices. The control center would act as an IoT based centralized real-time monitoring system that would enable predictive maintenance of the devices with the objective of eliminating downtime and optimizing cost. WinWire helped them accelerate the innovation process using Microsoft’s Hololens as a remote monitoring tool for IoT devices using Azure.
WinWire’s solution used HoloLens as a technical platform and built a dependable solution that provided recommendations and strategic health assessments by monitoring the assets through IoT sensors and system data. They implemented end-to-end real-time data ingestion pipeline and Mission Control Center (MCC) dashboards, enabling real-time monitoring of the health devices and narrowing down to a specific device to fetch service ticket details.
The solution integrated customers’ custom asset health score and other analytics models to identify the health of the devices as well as SAP-based ticketing system to automatically create service tickets. It helped the client not just optimize cost and operations, but also drive efficiency and achieve zero downtime through real-time monitoring and predict maintenance of devices.
Success stories like this one help us realize how MR is helping organizations pace up their endeavors and make MR devices an integral part of their technological infrastructure to all-round improvement in their services and well as operations.
Sources: