What is Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing is a sort of security analysis that examines an application’s vulnerability. Pen Testing is another name for penetration testing. Pen testing is done to identify any potential security risks in the system. Pen Testing is a method that employs the same strategies and tools that a hacker would use to test, evaluate, and enhance the security mechanisms of an Organisations’ networks and systems. Pen tests can be carried either manually or automatically using software programmes.
Why Penetration Testing?
The purpose of penetration testing is to determine whether a hacker can access administrative profiles, exploit technology for nefarious purposes, introduce and propagate malware, or access sensitive information. These tests help create software, ensure that it complies with security standards, and guard against malware infections and online attacks. Most firms periodically conduct security testing, especially those that handle client data.
Few advantages of penetration testing
- The results of penetration testing are used to assess the security flaws in your network infrastructure or application system configurations. A pen test also checks at the routine and daily activities of employees that might facilitate malicious penetration and security breaches. After the testing is complete, a report outlining all the flaws and suggesting software and hardware upgrades are drafted. Advice on provided policies that would improve in security general.
- Through penetration testing, Organisation acquires more knowledge about the techniques that hackers might use to access the systems and improve contingency planning. Using this information, Organisations can come up with programmes, systems, and other technologies that can protect systems against malicious activities.
- Any business activity must have access to resources, constant communication, and network availability in order to operate unceasingly. The organisation will weaken if these necessities are compromised. Similar to a business continuity audit, a penetration test looks for potential vulnerabilities that could cause unanticipated outages or accessibility loss. By addressing these threats, pen test guarantee uninterrupted business operations.
- Although penetration testing typically necessitates an investment, it additionally possesses the ability to save the firm much more money. Depending on the extent and nature of the breach, data breaches can be catastrophic, but penetration testing can be a valuable investment to mitigate this expense.
- Cyberattacks and data breaches have a detrimental impact on client loyalty and confidence. The stockholders would sense greater safety if the organisation is acknowledged for conducting out robust and formalised reviews and penetration tests.
Six ways to perform Penetration Testing
There are many methods for penetration testing, few to name are:
1. Black box
The vulnerabilities in a system that can be exploited from outside the network are identified through a black-box penetration test. When working on a black-box testing assignment, the penetration tester simulates the profile of a characteristic hacker with no insider knowledge of the target system. Architecture diagrams and non-publicly accessible source code are not provided to testers.
Black-box penetration tests are indeed the quickest to accomplish due to the penetration tester’s minimal knowledge since the task’s accomplishment relies significantly on the tester’s ability to recognize and take advantage of vulnerabilities in the target’s openly facing services. The primary disadvantage to this approach is that any vulnerabilities in internal services remain unrecognized and unpatched if the testers failed to breach the perimeter.
2. White box
White-box testing is the most time-consuming kind of penetration testing since its major difficulty is filtering through the vast quantity of data available to find possible potential vulnerabilities. The suitable approach for calculation testing is white-box penetration testing, which offers a complete analysis of both internal and external vulnerabilities.
White-box pen testers have a close working interaction with developers, allowing them to have access to Source code, architecture manuals, and other materials, which offers them a considerable level of system expertise but may also influence how they perform as they utilize data that hackers lack.
3. Gray box
A Gray-box tester often has administrative privileges on a system and has the accessibility and understanding of a user. Gray-box pen testers often have some knowledge of the internals of a network, possibly including design and architecture documentation and an account internal to the network.
Gray-box pen testing is used to evaluate a network’s security and is intended to do it in a more concentrated and effective manner than black-box testing. Pen testers can save time by using the network’s design documentation to concentrate their assessment efforts on the systems that are most valuable and at risk from the beginning. An internal user account on the system enables security testing within the fortified perimeter and simulates an intruder with prolonged access to the network.
4. External
A technique called external penetration testing evaluates an organisation ’s information that are exposed to the external world. A specialised group of Security researchers conducts external penetration testing independently.
In an external penetration test, the tester uses system vulnerabilities on the external assets to attempt to hack through the internal network. As an alternative, the tester may attempt to gain access to privileged data through resources that are visible to the public, like email, websites, and file shares. In order to gather data on all assets associated with the test, the attacker conducts investigation on the in-scope assets. Open ports, vulnerabilities, and basic information about the users of the company are all included in this intelligence for password attacks. Once the perimeter has been successfully hacked, the tester moves on to the internal penetration test after the external penetration test’s goals have been met.
Security testing can be delegated economically. External penetration testing is excellent at emulating a hacker’s activities on the target system and offers an entirely novel viewpoint on the security of the system. Due to the fact that it is an outside engagement, conducting frequently of such tests is typically time consuming.
5. Internal
Internal security researchers perform penetration testing on internal systems. A full-time security team’s upkeep can be expensive. In-house security experts frequently find it difficult to evaluate a system from a hacker’s point of view because they are acquainted with its intricacies. Internal penetration tests are simpler to organize and can be performed more often.
Internal penetration testing extends the assessment, in determining the extent to which an attacker may progress laterally across a network once an external breach has occurred.
Security risks within a company are considerable and frequent. Internal pen testing aids in locating and plugging security holes and vulnerabilities that an attacker might use to get beyond their initial access point to their intended target.
6. Blind
In such tests, the ethical hacker is simply provided with the name of the company whose systems they are testing without any further details. The aforementioned type of penetration test, also alluded to as the closed-box penetration test, provides software teams a real time simulation of how a malicious invader approaches the system.
Apart for the security experts and IT team who will be defending against the attack in this scenario, virtually no one at the target firm is notified of the test. The efficiency of an organization’s internal security monitoring systems can be assessed with the help of this kind of test.
Lifecycle of Penetration Testing
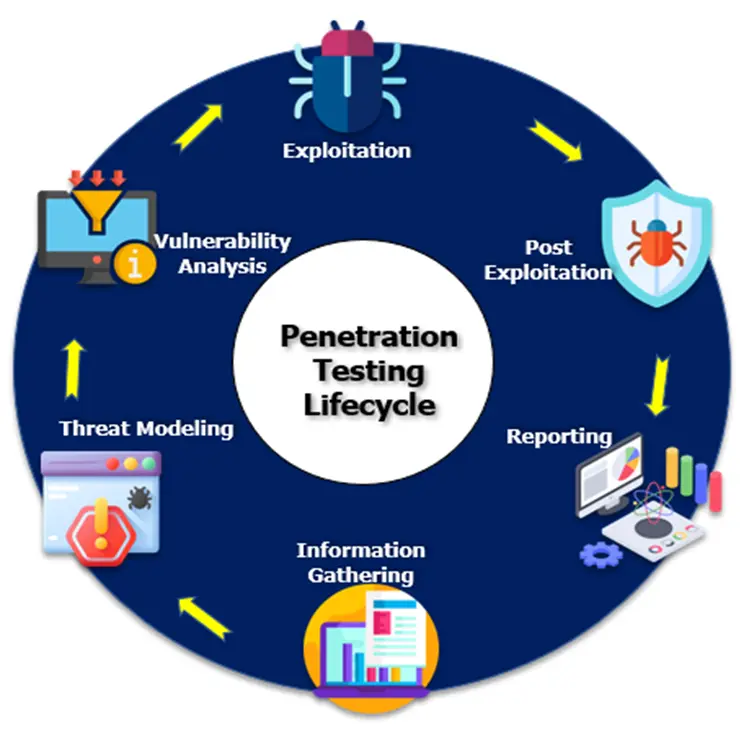
- Pre-engagement activities:
1.a Reconnaissance:
This involves learning everything there is to know about the intended system, including its architecture, hardware and software components, services, and ports that are accessible.
1.b Scanning:
This involves using automated tools to scan the target system for potential vulnerabilities.
This is typically done using following.
- Static Analysis – Inspects the application source code before a program is run by comparing it to a set of coding rules followed by debugging.
- Dynamic Analysis – is the testing and assessment of the security system by employing real-time data executions. By employing automated security scanning tools to scan the application or systems, the objective is to identify faults or vulnerabilities in real-time. After static or dynamic analysis, vulnerabilities or errors are manually verified to weed out false positives.
- Exploitation:
This entails using the vulnerabilities that have been discovered or initiating an attempt to enter the system using the appropriate user privileges. This is the stage where the main damage is completed. The attacker will undertake attempts at stealing the data, launch DoS assaults, compromise the system, etc (a resource that will steer you through cyber-security attacks). In an essence, this phase is regulated in a pen test to ensure that the network mayhem is constrained.
- Risk Analysis and Reporting:
Risk analysis’s goal is to learn further about and record the methodology utilised to acquire the crucial data that belongs to the organization. The pen tester must be capable of assessing the value of the compromised systems and any value associated with the confidential data captured.
Reporting entails recording the tests and vulnerabilities that were exploited, sensitive information that was compromised and accessed, the duration that the security tester could remain in the system before being detected and give recommendations for enhancing the system’s security.
Styles of Penetration Testing
There are two different styles to identify the vulnerability in an organization’s cybersecurity strategy.
Red Team: The red team concentrates on breaching the system in order to detect security flaws and evaluate the efficacy of the organization’s security protocols. In order to access sensitive information, applications, and systems, the red team takes advantage of flaws in the system, including those related to authorization and authentication. Also, they check for places where an attacker could deceive and gain access through social engineering.
Blue Team: The blue team attempts to thwart the red team penetration into the system. To identify possible risks, they employ a wide range of methods, including patching and upgrading systems, setting up firewalls, and analysing logs. Additionally, they evaluate the system to find any vulnerabilities that the red team might have overlooked or ignored.
These teams are essential for evaluating an organization’s security and assuring it is safeguarded against potential threats. The blue team tries to mitigate the risks while the red team concentrates on identifying the system’s vulnerabilities. They collaborate towards safeguarding systems, applications, and data for organizations.
Scope of Automation in Penetration Testing
The technique of performing automated scans on a target system in order to identify any significant faults or vulnerabilities is known as automated penetration testing. These automated technologies often detect more vulnerabilities than manual testing and can deliver a comprehensive picture of the system. Furthermore, automated testing may offer a cost-effective solution to accomplish the tests whilst still saving time and resources. Automation technologies can hasten up the procedure and simplify the process to trace vulnerabilities.
Some common tools include:
- Nmap, a network scanning tool.
- Metasploit, a framework for automated exploitation.
- Aircrack-ng, a suite of tools for wireless security auditing.

These technologies can be used to scan networks, find security vulnerabilities, and detect any potential breaches for unwanted access. However, as automated tools might not be able to find every potential vulnerability, they should be used in conjunction with manual processes.
Penetration Testing vs Ethical Hacking
Pen testing, also characterized as penetration testing, is frequently confused with ethical hacking. Yet, there is always a thin line of significant distinction between the two terms.
| Penetration Testing | Ethical Hacking |
| Testing is solely done to make sure the system is secure. | One of its characteristics is penetration testing. |
| Required to have the knowledge of only the specific area for which the tester conducts pen testing. | A thorough understanding of hardware and software programming is required for testing by an ethical hacker. |
| Any tester who has experience with penetration testing may conduct a pen test. | To be effective, one must be a subject-matter specialist with the necessary ethical hacking certification. |
| Compared to ethical hacking, there is less reporting and paperwork. | There must be thorough documentation, including legal agreements, etc. |
| This sort of testing takes less time to complete. | Comparatively speaking to penetration testing, ethical hacking takes a lot of time and effort. |
| Accessibility is required only for the part for which the tester performing pen testing. | Requires a whole range of accessibility to all computer systems and the infrastructure that supports them. |
Real time case studies to uncover the vulnerabilities using penetration testing
CASE 1- Payment Gateway information discloser
Problem Statement:
An unsupervised environment releases sensitive user information while performing Payments using unnamed gateway and same information is reused for hacking and crime against the server and user.
Solution Applied:
Using Penetration testing methodology, a team of professional testers performs an external penetration test on payment processing mechanism and supportive API’s. The test involves identifying maliciously information and residues on client and server side. Scanned all the authorization mechanism and find the API webhook pointers. By using filter file operator for read and write manipulation with tweaking API keys, the exploitation facilitates resolved the problem.
These findings are scanned by using Penetration testing and dev team fixed based on the best practises.
CASE 2- Web Application with specific domain Migrating on Cloud platform.
Problem Statement:
A well-known product firm wanted to Migrate a web application Migrated on Microsoft Azure cloud platform. The product is widely utilised and has clients all around the world. Stakeholders wanted to run a thorough web application penetration test to secure from cyber threats and Network vulnerabilities.
Solution Applied:
API’s are widely used in cloud services to communicate information across numerous applications. However, vulnerable API’s can also lead to a large-scale data leakage and cyber threat. Inappropriate access control and absence of data sanitization are also the main causes of data getting compromised which was uncovered during cloud penetration testing. The Test identified cloud server misconfigurations are improper access controls, not encrypting the data while communicating, and discrepancy in private and public data. The Pen test found also inadequate coding practices, weak passwords and includes bugs like SQLi, XSS, CSRF. These all are identified and provided team to fix and then we called complete migration on Cloud.
Takeaways from the above examples
- Utilizing a passphrase in password is encouraged rather than creating a basic password that’s capable of being guessed easily or a complicated password that is hard to recall.
- Stronger security and access controls and apply restrictions to the most delicate and significant data and network. The delicate and significant resources should only be accessible to a selected group of individuals.
- Ensure use latest certificates, coding best practice’s and fix all leak and loss pointers, to enhance security, consider implementing hardware and multifactor authentications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Penetration Test
Advantages:
- The main advantage of penetration testing is the early identification of problematic access points and vulnerabilities in the system and networks.
- Once the vulnerabilities have been found, a black hat hacker can use them to access the systems and network, find areas that require improvement, and devise strategies and tools to thwart and lessen attacks.
- Millions of dollars in harm could result from a straightforward security system breach. Penetration testing can shield your business from these harms.
- A considerable penalty for non-compliance may be eliminated with the full records of pen testing.
- Pen Test certifies continued assiduity and perseverance by carrying the required security checks.
Disadvantages
- Penetration testing’s main drawback is that it can be an expensive and time-consuming operation.
- There is also a chance that not all system vulnerabilities could be found by the tests, which could result in significant security lapses.
- Moreover, because it necessitates the disablement of specific security elements during the testing process, penetration testing can also interfere with regular business activities.
Conclusion:
Given the rapid evolution of technology, system security is crucial, and penetration testing needs to be performed more frequently to reduce the likelihood of an effective assault.
Organizations trying to protect the security of their networks and applications should consider penetration testing as a key tool. But it’s crucial to balance penetration testing’s expenses and potential hazards with the security advantages it offers.






