Managing translations for your app can be a real headache. You’re juggling multiple languages, file formats, and constant updates. It’s easy for things to get chaotic fast. But what if there were a way to simplify the whole process without losing your mind?
That’s where our Google Translation Service API comes in. It’s designed to make translation management easy, flexible, and scalable, whether you’re a solo developer or part of a large team.
In this post, I’ll walk you through how it works step by step and how it can save you time, hassle, and frustration.
Getting Started: TSV, .JSON Files as Your Source
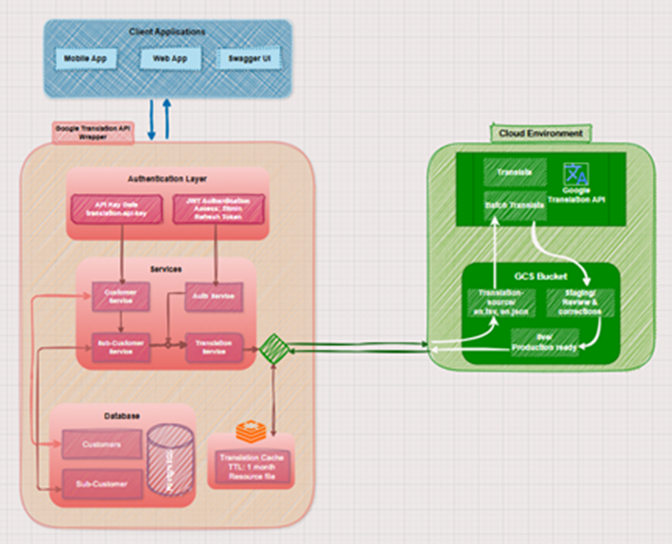
So, first things first. You probably already have an English translation file, something like en.tsv, en.json. This file is basically a list of key-value pairs. The key is some identifier for the text (like a button label or a message), and the value is the actual translation.
Why TSV, though?
TSV is chosen because it’s simple, lightweight, and universally readable. Unlike JSON, which can be nested and complex, TSV is just a plain text format where each piece of data is separated by tabs. That makes it easy to:
- Open and edit in common tools like Excel, Google Sheets, or any text editor.
- Avoid compatibility issues, no need for special software or knowledge of data structures.
- Prepare and upload easily to APIs, especially when dealing with structured data like source and translated strings.
JSON can get complicated with nesting, encoding, or special characters, which may not be ideal for batch translation or bulk uploads. TSV keeps things flat and clean, perfect for straightforward, large-scale translations.
Upload: Your Translation Starting Point
Before anything else, you upload your source file typically something like en.tsv to the system.
This file acts as your master reference for all other languages. Once uploaded, the file is validated, stored in the right project folder, and prepped for the next step.
Initiate: Kick Off the Translation Process
Once the source file is uploaded, the next step is to initiate the translation.
In this step, you specify the source language (usually English), select the target languages (like French, German, or Japanese), and link the uploaded file to the translation job.
This triggers the translation process behind the scenes. The system determines whether to use real-time or batch processing and begins preparing the data for staging.
We use two key Google Translation methods here:
- Translate: Best for short strings or quick, one-off text — perfect for real-time needs or basic testing.
- BatchTranslate: Built for large files with hundreds or thousands of strings. This is what powers our high-volume bulk translations efficiently.
By choosing the right method automatically, the system makes sure the translation is both fast and resource-friendly.
Translate and Review: The Stage Translation Process
After the initiation, translated content is stored in a staging area, not pushed live yet.
This staging phase is all about quality control. While Google’s machine translation is powerful, it’s not always perfect. Context, phrasing, and tone still matter, and staging gives you a chance to:
- Review translations before going live
- Manually tweak any inaccuracies
- Collaborate with reviewers or linguists to ensure localization quality
Nothing gets published until it passes your review.
Finalizing: Push It Live
Once you’re confident that the translations in staging are accurate and polished, it’s time to finalize and push them live.
At this stage:
- Translations are locked and published to production
- The system generates .json and .tsv files for each target language
- These .json files are structured in a way that your app can easily consume
The finalized .json files are what your app references when rendering multilingual content. The .tsv versions are still available for export, backup, or future edits.
Speed It Up with Redis Caching
Let’s talk about the performance. Once translations are finalized, speed becomes essential, especially if your app serves users globally.
That’s why we cache the finalized .json translation files in Redis.
This ensures:
- Translations load instantly, with zero lag
- Your app doesn’t need to fetch translations from cloud storage on every request
- Lightning-fast performance for localized content
Redis turns a potentially slow translation fetch into a blazing-fast in-memory call — perfect for responsive UIs and global audiences.
Scalable and Multi-Customer: Plug-and-Play for Any Size
The translation service isn’t just fast; it’s built to scale.
Whether you’re managing a single app or an entire product ecosystem, the system is fully multi-customer. That means each project or application remains isolated, with separate storage, staging, and translation paths, ensuring no mix-ups or conflicts.
- Plug-and-play: Simple integration into your app architecture
- Scalable: Handles 1 language or 100, no problem
- Isolated: Each customer’s data is safe and separate
It’s designed for both startups and enterprises alike.
Behind the Scenes
We’ve also built some handy utilities to keep things organized, automated, and low-maintenance:
- TSV to JSON Converter: Converts your flat.tsv into a structured .json format, the API can easily process
- Centralized Error Handler: Catches and returns standardized error responses, making debugging consistent and simple
- Cloud Storage Helpers: Handles uploading, renaming, organizing, and deleting files in cloud buckets, no manual file ops needed
- Redis Cache Manager: Automatically caches finalized .json translations in Redis for ultra-fast lookups
The Translation Process in a Nutshell
Let’s recap the entire flow from start to finish:
Upload the Source File
You begin by uploading your en.tsv file the source of truth for your app’s content.
Initiate Translation
Next, you start a translation job by selecting the source and target languages. This triggers translation using Translate or BatchTranslate, depending on the workload:
- Translate: For simple text or single sentences
- BatchTranslate: For bulk strings or full-file translations
Stage Translation
All translated content is moved to a staging area where you can review, refine, and collaborate before publishing.
Finalize and Publish
Once reviewed, translations are finalized and pushed live as .json and .tsv files. The .json files power your multilingual app.
Redis Caching
Finalized .json files are cached in Redis, delivering ultra-fast translation fetches directly to your app.
Final Thoughts: Easy, Flexible, and Fast
So, there you have it. Managing translations doesn’t have to be a nightmare. With our Google Translation Service API, you get the flexibility to work with simple TSV files, initiate translation jobs effortlessly, review everything in staging, and go live confidently, all while delivering fast performance with Redis.
Whether you’re a solo dev or managing translations across a big team, this service takes the complexity out of localization. It’s built to save you time, reduce errors, and scale as your app grows.






