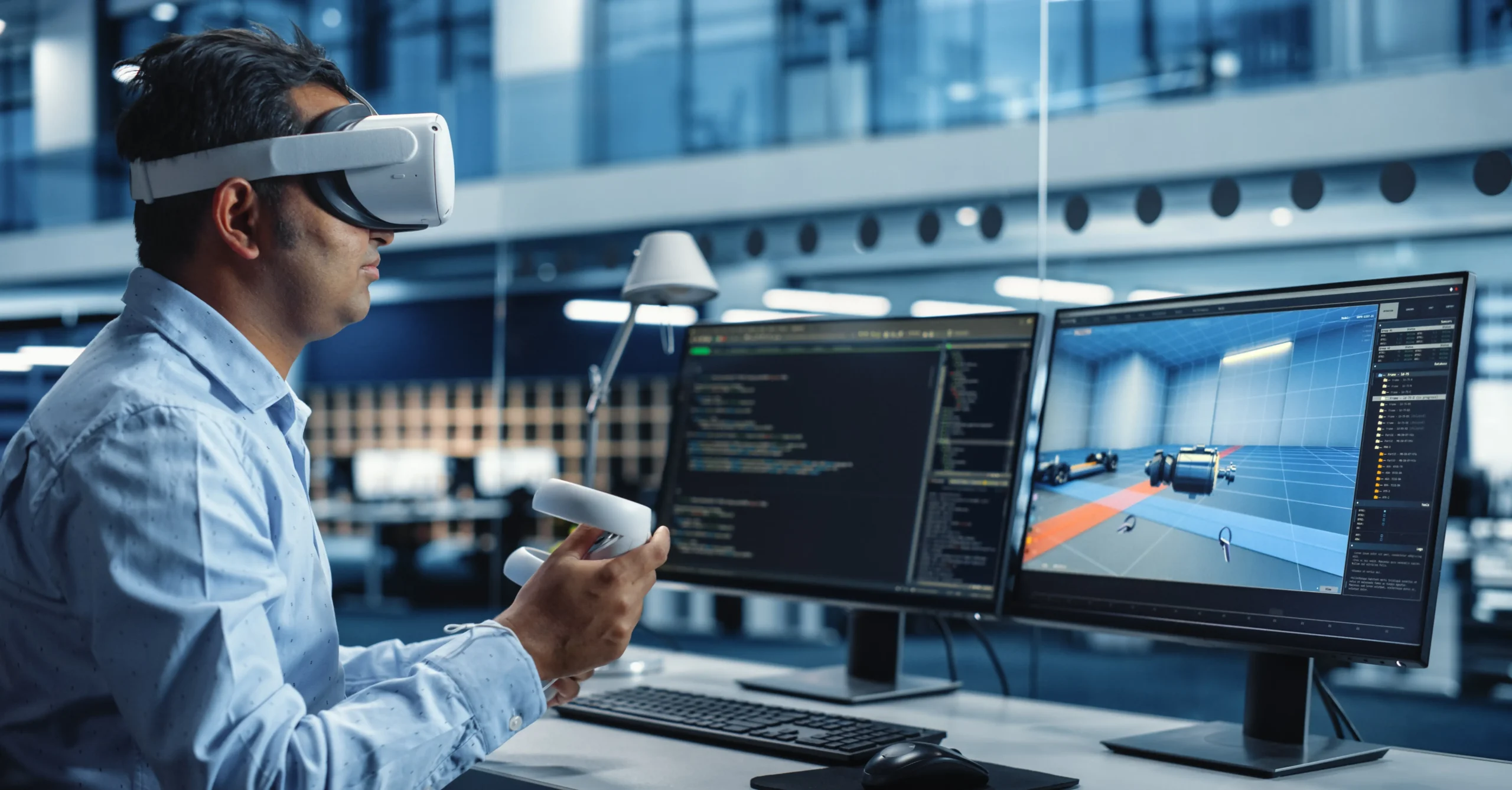
Technology has evolved from screens to immersive experiences. Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and the Metaverse are revolutionizing how we interact, learn, shop, and socialize. With this rapid adoption, testing these environments becomes crucial to ensure performance, usability, accessibility, and security.

What is Augmented Reality (AR)
AR is a technology that overlays digital information, such as images, sounds, or other data, into the real-world environment in real time. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which creates an entirely virtual environment, AR enhances your perception of the real world rather than replacing it.
- Example: IKEA’s AR app that allows users to visualize how furniture items will look and fit in their homes before making a purchase.
How Augmented Reality works
Scene Capture: AR devices (such as smartphones) use cameras and sensors to capture the environment, including gyroscope, accelerometer, GPS, and depth sensors to understand position, orientation, and spatial mapping.
- Environment Recognition: AR software analyzes the captured scene to detect surfaces, edges, and objects. Like -Marker-based QR codes, Projection-based, Location-based.
- Virtual Object Placement: Once the environment is analyzed, AR software calculates the position, scale, and orientation of digital objects.
- Rendering: AR devices render virtual content on displays in real time. Like- Rendering includes lighting, shadows, and occlusion to make virtual objects blend seamlessly with the real environment.
- User Interaction: Many AR systems allow users to interact with digital content via gestures, touch, voice, or device movement. Interaction data is processed in real time, dynamically updating the AR scene.
What is Virtual Reality (VR):
VR is a technology that creates a simulated, immersive environment that users can interact with in a seemingly real way. Unlike traditional screens, VR aims to make you feel like you are “inside” the environment, rather than just looking at it. It’s widely used in gaming, education, training, architecture, healthcare, and even social interactions. VR creates a fully immersive simulated environment that users interact with using headsets and controllers.
- Example: Oculus-based VR gaming, Oculus devices are specialized VR headsets that immerse players in 3D virtual environments.
How Virtual Reality works:
- VR Headset: A headset with screens provides a field of view and depth perception, making visuals look more realistic.
- Motion Tracking: Sensors in the headset, controllers, or room track head, hand, and body movement.
- Controllers / Input Devices: Some advanced systems track finger movement for more natural interactions.
- Audio & Haptics: Haptic feedback (vibrations, pressure) enhances the feeling of touch.
What is Metaverse?
The Metaverse is a term that refers to a collective virtual shared space that merges physical reality, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) to create immersive, interactive digital environments. Think of it as the internet evolving from being just 2D websites and apps into a 3D, interactive universe where users can socialize, work, play, and even trade digital assets. A persistent, shared, 3D virtual world where AR and VR converge with social, economic, and cultural interactions.
- Example: Meta’s Horizon Worlds- Designed to allow users to explore, create, and interact within immersive 3D environments
How Metaverse works?
- Virtual Reality (VR): Uses headsets like Oculus Quest to immerse users in fully digital 3D worlds.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Overlays digital content on the real world using smartphones, AR glasses, or tablets.
- Blockchain & Cryptocurrencies: Powers ownership of digital assets through NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens). Enables digital marketplaces and virtual currencies for buying/selling virtual goods.
- Cloud Computing & Edge Computing: Hosts large-scale virtual worlds and ensures low-latency interactions across the globe. Handles real-time data processing for thousands of users simultaneously.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Creates intelligent NPCs (Non-Player Characters) or dynamic environments. Helps with personalization and moderation within the Metaverse.
- Social and Collaboration Platforms: Platforms like Roblox, Fortnite, Decentral, and Horizon Worlds allow social interaction, gaming, and commerce within shared virtual spaces.
Testing AR, VR, and Metaverse for a smooth user experience, which is essential to adoption.
Real-World Use Cases
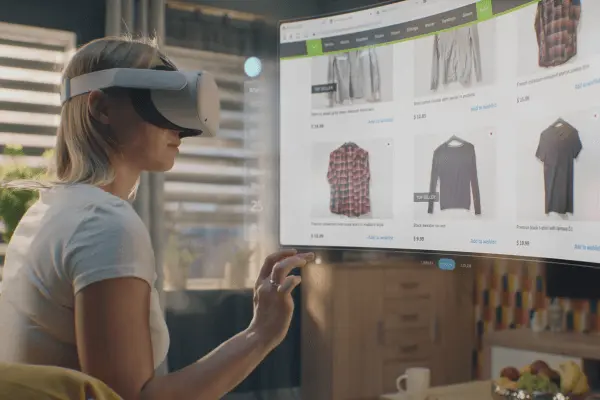
Retail (AR Shopping Apps): Sephora’s AR try-on app- It allows users to virtually apply makeup products, including lipsticks, eyeshadows, blushes, and false lashes to their own faces in real-time using their smartphone’s camera.

Manufacturing (AR-assisted Maintenance): AR Glasses Hardware: Equipped with cameras, sensors, and displays to capture the technician’s view and overlay digital content. Help in Shows step-by-step instructions. Highlights parts to repair. Detects mistakes or missing parts. Can record or stream work for remote supervision.
- Technicians use AR glasses to get live assembly instructions.
- 60% faster troubleshooting, 45% reduction in human errors.
Healthcare (VR Training Simulations): Osso VR and PrecisionOS software offer a comprehensive platform for surgical training and assessment. It provides realistic, hands-on simulations across multiple specialties, integrating with analytics to track performance.
- Surgeons practice VR environments before real surgeries.
- Cuts training time by 30 to 40%, reduces real-world errors by 25%.

Entertainment (VR Gaming ): Fortnite’s VR uses virtual reality (VR) technology to experience Fortnite in an immersive 3D environment.
Beat Saber – A VR rhythm game where players slash blocks to the beat of music using lightsabers.
Half-Life: Alyx – A VR first-person shooter set in the Half-Life universe, focusing on immersive combat and physics-based puzzles.
- Help in hosting concerts for millions of attendees.
- Eliminates geographical barriers, saving 100% on travel logistics.
Education (Metaverse Classrooms): Roblox Education leverages the platform to transform learning into an interactive and engaging experience. Key aspects include -Immersive Learning, Community Fund, Learning Hub, and Curriculum Integration.
ClassVR provides a comprehensive virtual reality solution tailored for schools that enhances engagement and knowledge retention. Its features include- Standalone VR Headsets, Curriculum Alignment, and Teacher Portals.
- Roblox and ClassVR campuses where students collaborate globally.
- 50% reduced dependency on physical infrastructure, global participation without travel.
Testing Checklist for AR, VR, and Metaverse
Here is a comprehensive checklist with real-time examples for testing AR, VR, and Metaverse applications/Software.
1. Functionality Testing
- Verify object placement and alignment in AR (e.g., IKEA AR furniture should not float or sink).
- Test navigation controls in VR environments (e.g., Meta Quest controllers respond correctly).
- Ensure Metaverse avatars interact correctly (e.g., handshakes, gestures).
2. Usability Testing
- Evaluate comfort of prolonged headset use (weight, eye strain).
- Accessibility: Voice-enabled navigation for differently abled users in Metaverse classrooms.
- Intuitive gestures: Ensure AR object rotation is smooth and accurate.
3. Compatibility Testing
- Cross-device: AR app works across iOS and Android versions.
- VR headsets: Support for multiple devices (Oculus, HTC Vive, PS VR).
- Metaverse platforms: Test interoperability (avatar consistency across different Metaverses).
4. Security & Privacy Testing
- Validate personal data encryption in Metaverse transactions.
- Test AR app permissions (camera, GPS access) to avoid misuse.
- Secure payment flows in VR shopping malls.
5. Localization Testing
- Test language overlays in AR-based retail apps.
- VR training simulations with localized instructions.
- Metaverse chat & voice translation accuracy.
7. Performance Testing
- Latency: Measure rendering delay (<20ms for VR to avoid motion sickness).
- Frame Rate Stability: Maintain 90+ FPS in VR headsets.
- Network Testing: Test Metaverse under varying bandwidths (e.g., 4G vs 5G).
8. Accessibility Testing
- Color contrast for AR overlays (for color-blind users).
- Voice-to-text captions in VR meetings.
- Haptic feedback for deaf individuals in Metaverse interactions.
Market Research ROI of AR, VR, and Metaverse Testing
AR (Augmented Reality), VR (Virtual Reality), and Metaverse platforms are immersive, interactive, and increasingly being used in gaming, training, e-commerce, simulations, and enterprise solutions. Testing these platforms is crucial due to:
- High user expectations for realism and interactivity.
- Complex integration of 3D graphics, haptics, AI, IoT, and networking.
- Risk of performance, usability, and security issues.
ROI calculation is based on cost avoidance, revenue generation, efficiency gains, and brand value.
- AR: Enables virtual product trials -reduces product return rates by up to 30%.
- VR: Provides immersive focus group studies – improves product design cycle by 20–25%.
- Metaverse: Allows large-scale, cost-effective consumer behavior analysis -reduces physical event costs by 70%.
Components of ROI to track
A. Cost Savings
- Reduced Post-Release Defects
- Early testing identifies glitches in VR interactions, AR overlays, or Metaverse environments. Prevents costly patches and user churn.
- Fixing a VR navigation bug before launch can save $50k–$100k in support and patch releases.
- Lower Support Costs
- Well-tested immersive platforms reduce customer complaints. Reduced helpdesk tickets for Metaverse onboarding issues.
- Avoiding Hardware Damage
- VR/AR apps interact with headsets and controllers; faulty design can lead to device damage. Testing reduces warranty claims or replacement costs.
B. Revenue Gains
- Better User Retention
- Smooth immersive experiences improve engagement and lifetime value.
- A Metaverse shopping experience with seamless AR try-on increases conversion rates.
- Faster Time-to-Market
- Automated testing and simulation environments accelerate release cycles. Early launch captures market opportunities.
- Enhanced Monetization Opportunities
- Metaverse platforms may include virtual goods, NFTs, or subscriptions. Reliable platforms encourage more transactions.
C. Efficiency & Productivity Gains
- Reusable Test Frameworks
- AR/VR automated test scripts (e.g., Unity tests, Unreal Engine tests) reduce repetitive manual testing.
- Cross-Platform Testing
- A single suite can validate apps across devices (Oculus, Vive, ARKit, HoloLens). Reduces redundant testing effort by 30–50%.
D. Brand Value & Risk Mitigation
- Positive Customer Experience
- Immersive, bug-free experiences improve reputation.
- Reduces negative reviews and social media backlash.
- Compliance & Safety
- Testing for VR motion sickness, AR spatial safety, or Metaverse privacy ensures regulatory compliance.
ROI Calculation Framework
| Metric | Before Testing | After Testing | ROI Impact |
| Post-release defect cost | $100,000 | $20,000 | 80% cost saving |
| Customer churn due to UX issues | 10% | 4% | Increased retention revenue by 6% |
| Time-to-market | 6 months | 4 months | Early revenue generation |
| Test automation reusability | 0 | 40% of test cases are reusable | Effort savings 30% |
Conclusion
AR, VR, and the Metaverse are no longer futuristic buzzwords; they are transforming industries. For businesses, testing these immersive technologies is not optional but essential to ensure seamless, secure, and accessible experiences. With structured checklists, ROI analysis, and real-world metrics, companies can harness these technologies to save costs, improve efficiency, and enhance end-user satisfaction. The future of testing is immersive, just as the experiences it supports are.